Speaker
Description
Photon-counting detectors (PCDs) are an emerging technology that provides energy-selective images for a single x-ray exposure. At this time when studies have begun to consider PCDs for industrial nondestructive inspection, it is significant to present a metric describing the imaging efficiency or performance of PCDs. In this study, we describe the imaging performance in terms of detective quantum efficiency (DQE) and report the results of DQE analysis for a sample PCD using a representative x-ray spectrum (70~kV and 21-mm Al filtration). The investigating PCD, a mosaic of eight small detector modules, employs two adjustable energy thresholds, and it possesses a function called an anticoincidence operation, which sums charges spread over four pixels into a pixel exhibiting the highest charge signal.
The DQE of a single-channel PCD operated with a single energy threshold, which is typically used to reject counts triggered by random pulses owing to electronic noise, is described by the conventional DQE form:
$\mathrm{DQE}_{\mathrm{sc}}(u)=\frac{\overline{c}^{2}\mathrm{MTF}^{2}(u)}{\overline{q}_{0}\mathrm{NPS}(u)},$
where $u$ (mm$^{-1}$) denotes the Fourier conjugate of the space variable $x$ (mm), and $\overline{q}_{0}$ (mm$^{-2}$), $\overline{c}$, $\mathrm{MTF}(u)$, and $\mathrm{NPS}(u)$ (mm$^{2}$), respectively, represent the average x-ray photon fluence incident on a detector, mean counts per pixel,modulation-transfer function, and noise-power spectrum. According to the recent works [1,2], the DQE formula for two energy bins, i.e. the low ($L$)- and high ($H$)-energy bins can be derived as follows:
$\begin{eqnarray*}\mathrm{DQE}_{\mathrm{mc}}(u) & = & \frac{\overline{c}_{L}^{2}\mathrm{MTF}_{L}^{2}(u)}{\overline{q}_{0}\left[\mathrm{NPS}_{L}(u)-\frac{\mathrm{NPS}_{X}^{2}(u)}{\mathrm{NPS}_{H}(u)}\right]}+\frac{\overline{c}_{H}^{2}\mathrm{MTF}_{H}^{2}(u)}{\overline{q}_{0}\left[\mathrm{NPS}_{H}(u)-\frac{\mathrm{NPS}_{X}^{2}(u)}{\mathrm{NPS}_{L}(u)}\right]}\\ & & -\frac{2\overline{c}_{L}\overline{c}_{H}\mathrm{MTF}_{L}(u)\mathrm{MTF}_{H}(u)}{\overline{q}_{0}\left[\frac{\mathrm{NPS}_{L}(u)\mathrm{NPS}_{H}}{\mathrm{NPS}_{X}(u)}-\mathrm{NPS}_{X}(u)\right]},
\end{eqnarray*}$
where $\mathrm{NPS}_{X}(u)$ represents the cross-NPS between the two energy images. If the magnitude of the cross-NPS is negligibly small, the DQE formula can be reduced to
$\mathrm{DQE}_{\mathrm{lin}}(u)\approx\frac{1}{\overline{q}_{0}}\left[\frac{\overline{c}_{L}^{2}\mathrm{MTF}_{L}^{2}(u)}{\mathrm{NPS}_{L}(u)}+\frac{\overline{c}_{H}^{2}\mathrm{MTF}_{H}^{2}(u)}{\mathrm{NPS}_{H}(u)}\right],$
giving a DQE form that is a linear sum of DQEs of low- and high-energy bin images or $I_{L}$ and $I_{H}$, respectively. The linear form of DQE of a PCD represents how efficiently the detector converts the X-ray quanta incident upon it to two energy-bin images independently.
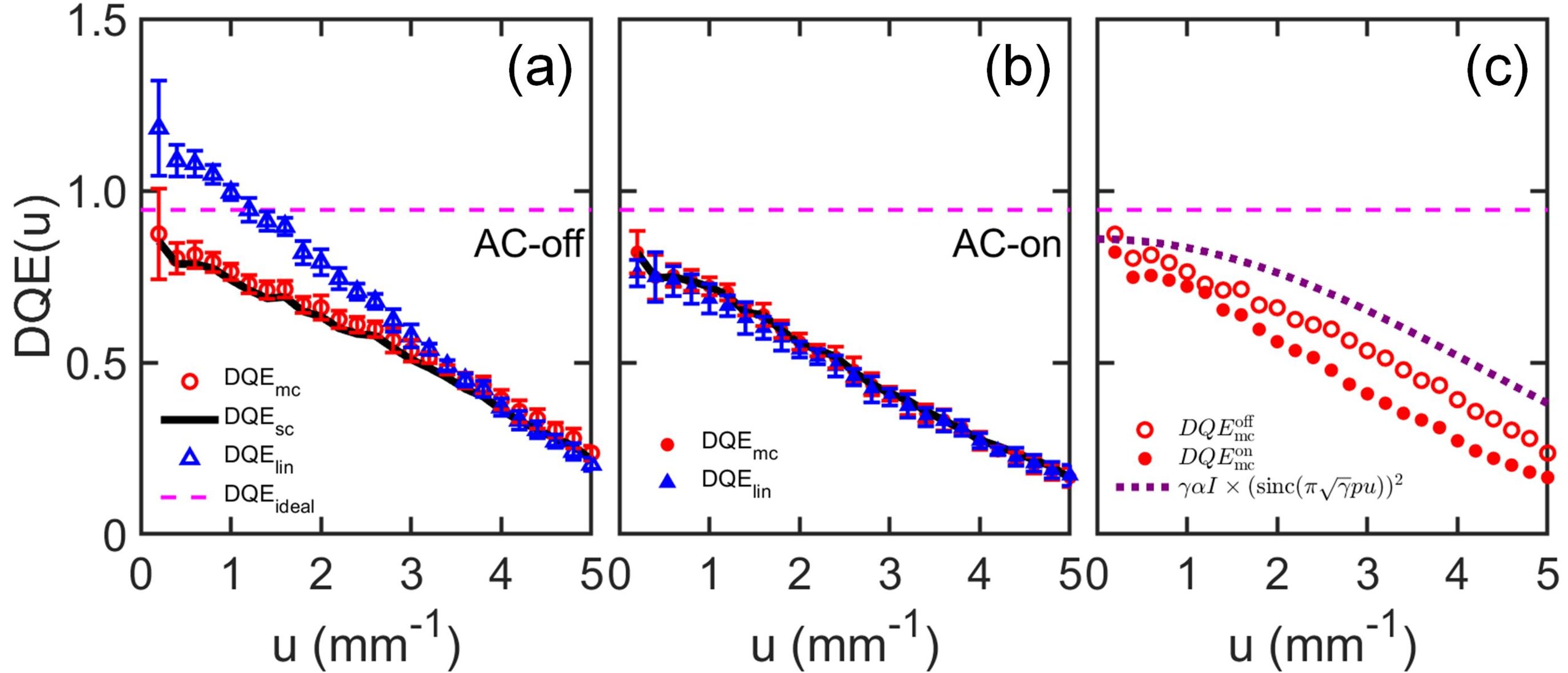
From the measurements of DQE, we verified that, without correction for the signal and noise correlation between energy bins, the DQE could be overestimated. The anticoincidence or charge-summing operation effectively suppressed the signal and noise correlations between energy bins, enhancing the MTFs and removing the cross-NPSs. However, it increased normalized NPSs in each energy-bin image, degrading the resulting DQE performance. The figure attached in this abstract shows the DQE results obtained using $\mathrm{DQE}_{\mathrm{sc}}(u)$, $\mathrm{DQE}_{\mathrm{mc}}(u)$, and $\mathrm{DQE}_{\mathrm{lin}}(u)$ for two different PCD operations: (a) AC-off and (b) AC-on. Plot (c) compares the DQE results obtained using $\mathrm{DQE}_{\mathrm{mc}}(u)$ for AC-off and on.
A discussion is given for describing the performance gap between the measured DQE and theoretical models. The DQE forms and analysis methodologies presented in this study will be helpful for researchers who want to understand their PCD-based imaging systems.
[1] J. Tanguay, D. Richtsmeier, C. Dydula, J. A. Day, K. Iniewski, and M. Bazalova-Carter, “A detective quantum efficiency for spectroscopic x-ray imaging detectors,” Med. Phy., vol. 48, no. 11, pp. 6781–6799, 2021
[2] N. Zarif Yussefian and J. Tanguay, “An experimental framework for assessing the detective quantum efficiency of spectroscopic x-ray detectors,” Med. Phys., vol. 50, no. 3, pp. 1318–1335, 2022
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (No. 2021R1A2C1010161), and conducted as a part of the research projects of “Development of automatic screening and hybrid detection system for hazardous material detecting in port container” financially (20200611) supported by the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries, Korea.
Corresponding author: hokyung@pusan.ac.kr